The old network can no longer handle your current Internet usage: the connection falters during an online work consultation and downloading large files takes forever. If this sounds familiar, your network is in need of an upgrade. Or maybe you're installing a wired network in a new building for the first time. In either case, you're faced with the choice of which utp cable to use from now on.
What is a UTP Cable?
A UTP cable is a network cable used for creating telephony and computer networks. UTP stands for Unshielded Twisted Pair. The cable consists of twisted pairs of conductors with a standard color code, essential for connecting the cable to a plug or wall socket.
The utp cable is strictly an unshielded cable. This means that the cable has no shielding against electromagnetic interference. However, UTP is usually used as a collective term for all network cables, regardless of shielding. And also the designations internet cable, Ethernet cable or twisted pair cable are used as a collective term for all cables that can transfer data.
Which internet cable do you need?
To install Internet or telephone cabling, you need a network cable. You then have the choice between the unshielded utp cable or the shielded network cable, such as the ftp (Foiled Twisted Pair), stp (Shielded Twisted Pair) or s/ftp cable. In addition, you can also choose different throughput speeds. This choice depends on the purpose of the network.
Using a shielded ftp cable is important when there are other COAX, power or power cables near the Internet cable. The use of foil in the ftp cable reduces the chance of connection or data transmission failure (interference) compared to an unshielded utp cable.
What is the difference between utp and ftp cables?
Using a shielded ftp cable is important when there are other COAX, power or power cables near the Internet cable. The use of foil in the ftp cable reduces the chance of interference in connection or data transmission compared to an unshielded utp cable.
Explanation of designations
The constructions of cables are designated by letters. Below we explain the difference between utp, ftp and stp cable.
U - Unshielded: without shielding.
F - Foil: shielding with foil around the wire pairs.
S - Braided: the wire pairs are shielded with braided metal.
With shielded wire pairs, there are two more variants:
UTP - the wire pairs are not individually shielded.
FTP - the wire pairs are individually shielded with foil.
With these designations, we create variants:
U/UTP: without shielding of wire pairs and without shielding per individual wire pair.
F/UTP: wire pairs equipped with aluminum foil, but without shielding per individual wire pair.
S/FTP: all wire pairs are protected with braided metal and each individual wire pair is shielded with aluminum foil.
To clarify this, the variations are shown below.
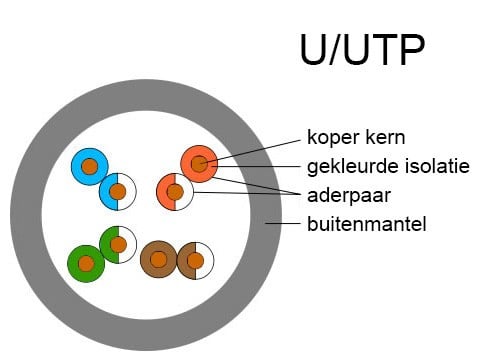
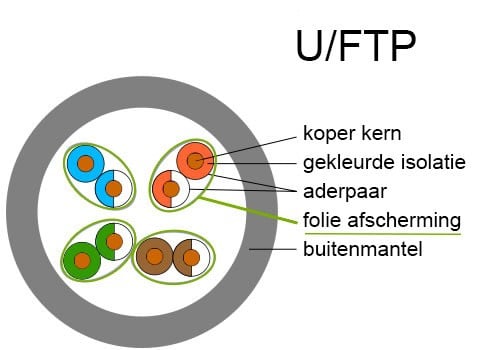
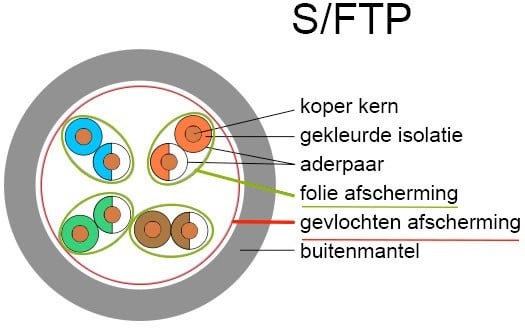
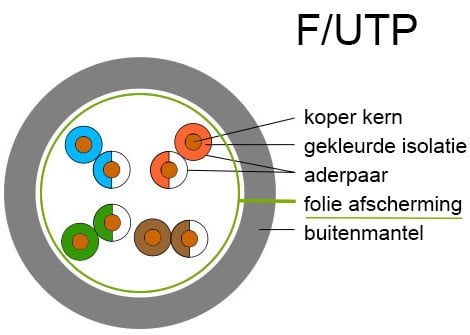
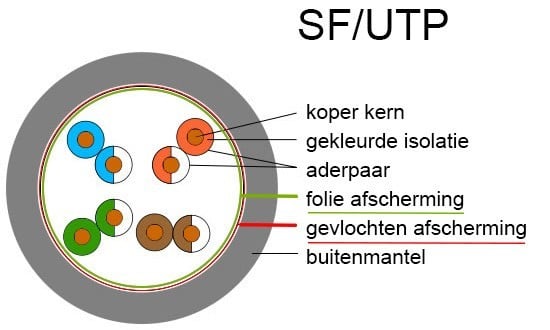
And each of these cable variants has its own specific speed. We refer to this specification as Cat.
To clarify the specification compositions, below is a table.
|
Old name |
New name |
Cable shielding |
Shielding wire pairs |
|
UTP |
U/UTP |
none |
none |
|
STP |
U/FTP |
none |
foil |
|
FTP |
F/UTP |
foil |
none |
|
S-STP |
S/FTP |
braid |
foil |
|
S-FTP |
SF/UTP |
foil,braid |
none |
The difference between Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a and Cat7
The rule of thumb for the speed of an Internet cable is: the newer/higher the category designation, the faster the cable. Below are the types of Internet cables.
|
|
Cable category | |||
|
Speeds up to |
1000 Mbit/s |
1000Mbit/s |
10.000 Mbit/s |
10.000 Mbit/s |
|
Suitable for network |
Gigabit |
Gigabit |
10-Gigabit |
10-Gigabit |
|
Throughput* |
100mhz |
250mhz |
500mhz |
600mhz |
The higher the mhz* number is, the more data is processed simultaneously.
What Speed Do You Need?
Which type of network cable and throughput speed you need depends on the situation for which you are using the network cable. Below we outline three situations in which we differentiate throughput speeds.
Home network: do you use internet cable alone or with the family? Then a Cat6 cable is sufficient in most cases. Are a lot of movies downloaded, series binge-watched and games played? Then we recommend going for the Cat6a, because the throughput offers just a little extra.
Charging station: if you plan to install a charging station at home or at the office, it is wise to lay a data cable in addition to the power cable. Even if you are not yet using a smart charging station with load balancing, this is the future. For this, it is best to use a shielded (S/FTP) Cat6 ground cable.
Home office and SME: Does the network connection need to be able to handle large up- and downloads from different employees? Or do you need to attend an important Teams meeting from the attic while your son or daughter is gaming? Then the network cable has a lot of data to process at one time. For these types of situations, we recommend the Cat6a cable.
Larger companies and IT networks: are you working with a large group of people on a network? Think customer service, sales, procurement and IT? Then the network has to work hard to transfer all the data quickly and without failures. With a Cat7 cable, your network can meet these challenges and you will be ready for the digital future.
What may already be noticeable is that the Cat5 cable is not explained. With today's 3-, 4- and 5G networks, the Cat6 has become the standard. The Cat6 cable reaches speeds of up to 1GB per second with a throughput of 250 mhz. That makes this a Cat6 cable the perfect cable for a home network.
But, do you want to prepare for the network of the future? And is this the time when you need to lay an Internet cable for an extended period of time? Then you can buy the Cat7 network cable just to be on the safe side.
Enough info?
If you have already made your choice, you can find some categories of utp cable below.
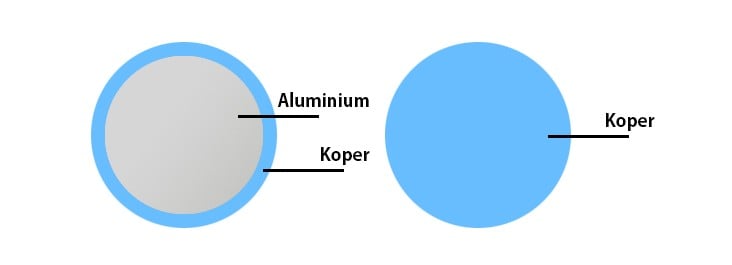
Buy CCA or 100% copper network cable
The speed of signal transmission depends on the conductor. You can choose between CCA or 100% copper conductor. A Copper Clad Aluminum (CCA) wire contains a copper wire, but has an aluminum core. With a 100% copper network cable, (as the name implies) everything is copper. On the outside, the CCA cable looks the same as a copper network cable. But copper cable has 5 key advantages.
- A copper cable retains its flexibility longer.
- Lower chance of cable breakage.
- A copper cable conducts signals better.
- Direct current (DC) resistance is lower.
- Complies with the ANSI/TIA-568-B2-1 standard.
To get the most out of a UTP cable, the maximum resistance should not exceed 9.38 Ohms DC per 100 meters at a wire thickness of AWG24 (0.205mm²). Copper is capable of achieving this. With this, a 100% copper cable offers optimum achievable speed and reliability for the respective UTP category.
The CCA network cable is a cheaper variant, which is also the main advantage of this Internet cable. Do you opt for the CCA cable? Then consider whether having a possible lower throughput and more chance of weak signal is problematic or not.
Note: Are you using PoE (Power over Ethernet)? Then we always recommend the 100% copper cable.
The difference between a flexible or rigid cable
When choosing the right UTP cable, you need to think beforehand about what you are terminating the network cable on. Because, this affects whether you buy a flexible or stiff network cable. A flexible or stiff cable has everything to do with the construction of the individual conductors.
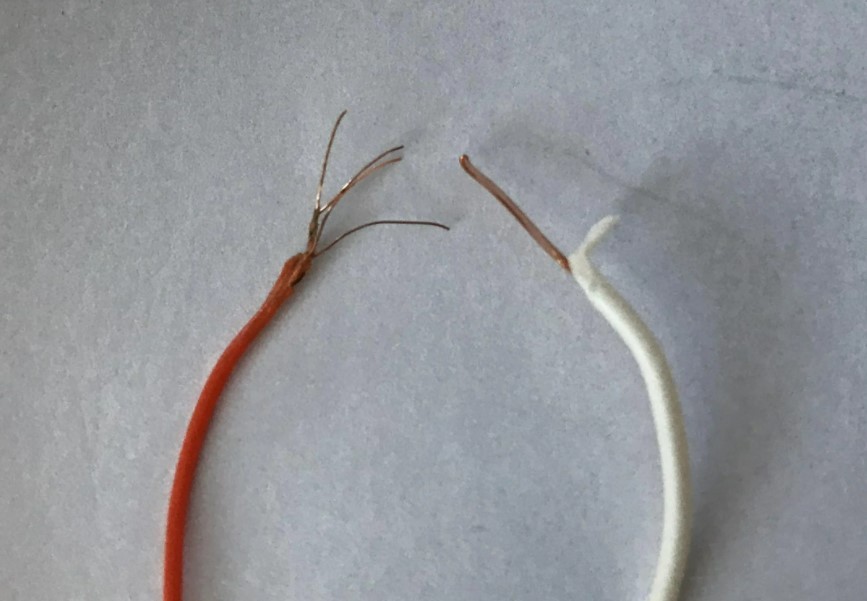
When you strip a UTP cable, you see 8 small conductors. When you strip these conductors individually, you can see the difference between flexible and rigid. A flexible cable consists of all smaller, copper wires (pictured on the left). A rigid cable consists of a single, solid wire (pictured on the right).
Connecting a UTP cable
Mounting a UTP cable can be done in two ways:
1. Connecting to the wall outlet or patch panel.
When terminating an Internet cable on a wall outlet or patch panel, the stiff cable is suitable. This cable adheres better to an LSA strip and thus provides the best possible connection. To terminate the stiff cable, use LSA pliers.
2. Connecting an RJ45 connector to the cable
When terminating an Internet cable to an RJ45 connector, the flexible cable is suitable. This is because the conductor of the RJ45 plug passes completely through the core of the conductor. This gives the best possible connection.
Note: Never mount an RJ45 connector on a stiff cable. The connector comes into poor to no contact with the solid conductors, creating the risk of the conductors shooting past the core. This results in a poor connection. Do you still want to mount an RJ45 plug on a stiff cable? Then choose only the plug that is suitable for the rigid cable. View Cat6a connectors for rigid cable here.
Quick start? Our advice for a home situation
As you have read, there is no general advice to give about which cable and connectors you will need to use for your situation.
But based on our common questions, we think the products below will get you started quickly in a home environment.
Need more information? We're here to help!